Granodiorite
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2020) |

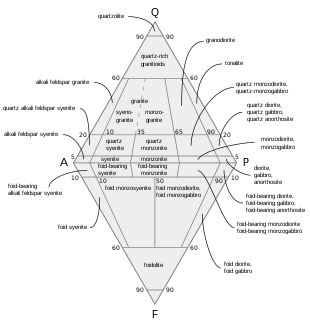


Granodiorite (/ˌɡrænoʊˈdaɪ.əraɪt, ˌɡrænəˈ-/ GRAN-oh-DY-ə-ryte, GRAN-ə-)[1][2] is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock similar to granite, but containing more plagioclase feldspar than orthoclase feldspar.
The term banatite is sometimes used informally for various rocks ranging from granite to diorite, including granodiorite.
Composition
[edit]According to the QAPF diagram, granodiorite has a greater than 20% quartz by volume, and between 65% and 90% of the feldspar is plagioclase. A greater amount of plagioclase would designate the rock as tonalite.
Granodiorite is felsic to intermediate in composition. It is the intrusive igneous equivalent of the extrusive igneous dacite. It contains a large amount of sodium (Na) and calcium (Ca) rich plagioclase, potassium feldspar, quartz, and minor amounts of muscovite mica as the lighter colored mineral components. Biotite and amphiboles often in the form of hornblende are more abundant in granodiorite than in granite, giving it a more distinct two-toned or overall darker appearance. Mica may be present in well-formed hexagonal crystals, and hornblende may appear as needle-like crystals. Minor amounts of oxide minerals such as magnetite, ilmenite, and ulvöspinel, as well as some sulfide minerals may also be present.
Geology
[edit]
On average, the upper continental crust has the same composition as granodiorite.
Granodiorite is a plutonic igneous rock, formed by intrusion of silica-rich magma, which cools in batholiths or stocks below the Earth's surface. It is usually only exposed at the surface after uplift and erosion have occurred.
Etymology
[edit]The name comes from two related rocks to which granodiorite is an intermediate: granite and diorite. The gran- root comes from the Latin grānum for "grain", an English language derivative. Diorite is named after the contrasting colors of the rock.
Banatite
[edit]Banatite is a term used informally for various rocks ranging from granite to diorite, but often granodiorite, that were intruded in the Late Cretaceous in the Banat and nearby regions of present-day Hungary and Serbia.[5] The term is also used in Australia in connection with Gulaga / Mount Dromedary in New South Wales, where it is described as "a rock of intermediate composition between quartz diorite and quartz monzonite".[6]
Occurrence
[edit]United States
[edit]Plymouth Rock is a glacial erratic boulder of granodiorite. The Sierra Nevada mountains contain large sections of granodiorite.
Egypt
[edit]Granodiorite was quarried at Mons Claudianus in the Red Sea Governorate in eastern Egypt from the 1st century AD to the mid-3rd century AD. Much of the quarried stone was transported to Rome for use in major projects such as the Pantheon and Hadrian's Villa. Additionally, granodiorite was used for the Rosetta Stone.
The extent of Egyptian granodiorite masonry is unclear. Egypt's 6000-year history makes determining the period of usage difficult as well. Perhaps like porphyry, it was ignored by the successive dynasties of Egypt and only heavily mined during Ptolemaic or Roman times. This is evidenced by the fact that most examples of granodiorite sculpture seem to have come from later dates. However, its presence in the Rosetta Stone implies that they had considerable experience with it and the fact that only newer artifacts are found may simply be because earlier pieces were lost.
Ireland
[edit]Granodiorite is quarried in the Newry area of County Armagh with the common name of 'Newry granite'.[7]
Uses
[edit]Granodiorite is most often used as crushed stone for road building. It is also used as construction material, building facade, and paving, and as an ornamental stone.[8] The Rosetta Stone is a stele made from granodiorite.[9] The portico columns of the Pantheon in Rome are formed from single shafts of granodiorite, each 12 metres tall by 1.5 metres in diameter.[citation needed]
See also
[edit]References
[edit] This article incorporates public domain material from Granodiorite definition. United States Geological Survey.[10][11].
This article incorporates public domain material from Granodiorite definition. United States Geological Survey.[10][11].
- ^ "granodiorite". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 2020-03-22.
- ^ "granodiorite". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 2016-01-21.
- ^ These rocks crystallized in depth from magma 300 million years ago. The original magma became deformed during cooling. Once the magma solidified, cracks opened in the rocks and were filled with residual magma, forming light-coloured dykes. Finally, as the magma cooled further, some of the dykes were themselves fractured in shear zones. See: Site of Geological Interest Roses Lighthouse (in Catalan, with a summary in English).
- ^ Elena Druguet and Jordi Carreras, Folds and Shear Zones at Cap de Creus, 2019, Field Trip Guide, Itinerary 2, at semanticscholar.org.
- ^ "Banatite". Mindat.org. 12 August 2021. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- ^ "Gulaga / Mt Dromedary Mining Heritage and Geology". Geological Sites of New South Wales. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- ^ "Newry By-pass". www.habitas.org.uk. Retrieved 7 August 2022.
- ^ Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer: Specialized Microscopy Techniques – Polarized Light Microscopy Gallery – Granodiorite. Micro.magnet.fsu.edu. Retrieved on 2015-11-19.
- ^ Image gallery: The Rosetta Stone. British Museum (2015-03-20). Retrieved on 2015-11-19.
- ^ "Granodiorite". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 2020-03-22.
- ^ "Granodiorite". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 2016-01-21.
External links
[edit] Media related to Granodiorite at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Granodiorite at Wikimedia Commons
