1920 Republican National Convention
| 1920 presidential election | |
  Nominees Harding and Coolidge | |
| Convention | |
|---|---|
| Date(s) | June 8–12, 1920 |
| City | Chicago, Illinois |
| Venue | Chicago Coliseum |
| Candidates | |
| Presidential nominee | Warren G. Harding of Ohio |
| Vice-presidential nominee | Calvin Coolidge of Massachusetts |
| Voting | |
| Total delegates | 984 |
| Votes needed for nomination | 493 |
| Ballots | 10 |
The 1920 Republican National Convention nominated Ohio Senator Warren G. Harding for president and Massachusetts Governor Calvin Coolidge for vice president. The convention was held in Chicago, Illinois, at the Chicago Coliseum from June 8 to June 12, 1920, with 940 delegates. Under convention rules, a majority plus one, or at least 471 of the 940 delegates, was necessary for a nomination.
Many Republicans sought the presidential nomination, including General Leonard Wood, Illinois Governor Frank Lowden and California Senator Hiram Johnson. Dark horse Harding, however, was nominated. Many wanted to nominate Wisconsin Senator Irvine L. Lenroot for vice president, but Coolidge was nominated instead, because he was known for his response to the Boston Police Strike in 1919.[1]
The convention also adopted a platform opposed to the accession of the United States to the League of Nations.[2] The plank was carefully drawn up by Henry Cabot Lodge to appease opponents of the League such as Johnson, while still allowing eventual American entry into the League.[3]
Presidential nomination
[edit]Presidential candidates
[edit]Potential or declined candidates
[edit]- Henry Cabot Lodge, U.S. senator from Massachusetts (declined to run)
- Henry Justin Allen, Governor of Kansas
- Albert J. Beveridge, former U.S. senator from Indiana
- William Borah, U.S. senator from Idaho
- Omar Bundy, General from Indiana
- T. Coleman du Pont, businessman from Delaware
- Will H. Hays, chairman of the Republican National Committee
- Charles Evans Hughes, former U.S. Supreme Court Justice, former Governor of New York, 1916 Republican candidate for President (declined to run)
- Myron Herrick, former Governor of Ohio
- Frank B. Kellogg, U.S. senator from Minnesota
- Philander C. Knox, U.S. senator from Pennsylvania
- Irvine Lenroot, U.S. senator from Wisconsin
- Edwin P. Morrow, Governor of Kentucky
- John J. Pershing, General of the Armies from Missouri
- Theodore Roosevelt, former President of the United States (died January 6, 1919)
- William Howard Taft, former President of the United States
- James E. Watson, U.S. senator from Indiana
- Frank B. Willis, former Governor of Ohio

At the start of the convention, the race was wide open.[5] General Leonard Wood, Illinois Governor Frank Lowden, and California Senator Hiram Johnson were considered the three most likely nominees.[6] Ohio Senator Warren G. Harding had been a front-runner, but his star had faded by the time of the convention.[6] Many expected a dark horse to be chosen, such as Pennsylvania Governor William Cameron Sproul, Pennsylvania Senator Philander C. Knox, Kansas Governor Henry Justin Allen, Massachusetts Senator Henry Cabot Lodge, or 1916 nominee Charles Evans Hughes.[5] Sproul in particular had been gaining momentum at the expense of Lowden, the candidate of the conservative wing of the party.[6] The issue of joining the League of Nations took center stage at the convention, with some speculating that Johnson would bolt the party if the platform endorsed the League.[6] The convention adjourned for the night after four ballots produced no clear leader, and many states stuck to favorite-son candidates.[7]

As the balloting continued the next day, Wood, Lowden, and Johnson remained in the lead, and party leaders worked to find a candidate acceptable to both the progressive and conservative wings of the party.[8] Conservatives strongly opposed Wood, while Lowden was opposed by the progressive wing of the party.[8] Harding emerged as a moderately conservative candidate acceptable to the progressive wing of the party, and as the convention remained deadlocked, Harding emerged as a strong compromise candidate.[8] After the eighth ballot, the convention recessed. During the recess, Harding's managers lobbied Lowden's supporters and others to support Harding.[8] Harding was also helped by the fact that the Democrats might nominate James M. Cox of Ohio, and Republicans did not want to give the Democrats a home state advantage in electorally critical Ohio.[9]

Harding jumped into the lead on the ninth ballot, and clinched the nomination on the tenth ballot. Many thought that Johnson could have stopped the Harding movement by throwing his support behind Knox, who could have displaced Harding as the compromise candidate. Johnson disliked Harding's policies and disliked Harding personally, and was friends with Knox. However, Johnson never released his supporters, and Harding took the nomination.[8][9]
| Presidential Balloting | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candidate | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9th | 10th[a] | 10th[b] | Unanimous |
| Harding | 65.5 | 59 | 58.5 | 61.5 | 78 | 89 | 105 | 133.5 | 374.5 | 644.7 | 692.2 | 984 |
| Wood | 287.5 | 289.5 | 303 | 314.5 | 299 | 311.5 | 312 | 299 | 249 | 181.5 | 156 | |
| Lowden | 211.5 | 259.5 | 282.5 | 289 | 303 | 311.5 | 311.5 | 307 | 121.5 | 28 | 11 | |
| Johnson | 133.5 | 146 | 148 | 140.5 | 133.5 | 110 | 99.5 | 87 | 82 | 80.8 | 80.8 | |
| Sproul | 84 | 78.5 | 79.5 | 79.5 | 82.5 | 77 | 76 | 75.5 | 78 | 0 | 0 | |
| Butler | 69.5 | 41 | 25 | 20 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Coolidge | 34 | 32 | 27 | 25 | 29 | 28 | 28 | 30 | 28 | 5 | 5 | |
| La Follette | 24 | 24 | 24 | 22 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | |
| Pritchard | 21 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Poindexter | 20 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 2 | 0 | |
| Sutherland | 17 | 15 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Hoover | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 10.5 | 9.5 | |
| du Pont | 7 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Watson | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Borah | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Knox | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ward | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Hays | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Kellogg | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Lenroot | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| MacGregor | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Warren | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Not Voting | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2.5 | 0.5 | |
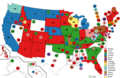
Presidential Balloting / 4th Day of Convention (June 11, 1920)
-
1st Presidential Ballot
-
2nd Presidential Ballot
-
3rd Presidential Ballot
-
4th Presidential Ballot
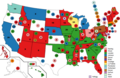
Presidential Balloting / 5th Day of Convention (June 12, 1920)
-
5th Presidential Ballot
-
6th Presidential Ballot
-
7th Presidential Ballot
-
8th Presidential Ballot
-
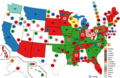
9th Presidential Ballot
-
10th Presidential Ballot
(Before Shifts) -
10th Presidential Ballot
(After Shifts)
The smoke-filled room
[edit]At the time, Harding's nomination was said to have been secured in negotiations led by party bosses George Harvey and Senator Henry Cabot Lodge in a mysterious "smoke-filled room" at Chicago's Blackstone Hotel." Legend says Harry M. Daugherty, Harding's political manager was the mastermind. After Harding's election he became United States Attorney General. On February 11, 1920, long before the convention, Daugherty predicted:
- I don't expect Senator Harding to be nominated on the first, second, or third ballots, but I think we can afford to take chances that about 11 minutes after two, Friday morning of the convention, when 15 or 12 weary men are sitting around a table, someone will say: 'Who will we nominate?' At that decisive time, the friends of Harding will suggest him and we can well afford to abide by the result."[10]
Daugherty's prediction described essentially what occurred, but historians argue that Daugherty's prediction has been given too much weight in narratives of the convention.[11] The "smoke filled room" was actually a suite rented by National Chairman Will H. Hays. For six hours the leaders considered numerous alternatives, including Wood, Lowden, and Johnson. However, there were objections to all of them. Headlines in the next morning newspapers suggested intrigue. Historian Wesley M. Bagby argues, "Various groups actually worked along separate lines to bring about the nomination - without combination and with very little contact." Bagby finds that the key factor in Harding's nomination was his wide popularity among the rank and file of the delegates.[12]
Vice Presidential nomination
[edit]Vice Presidential candidates
[edit]Before Harding was nominated, Johnson, Kansas Governor Henry Justin Allen, Massachusetts Governor Calvin Coolidge, Wisconsin Senator Irvine Lenroot, Kentucky Governor Edwin P. Morrow, and Harding himself were all seen as possible vice presidential nominees.[8] Once the presidential nomination was finally settled, Harding and the party bosses asked Johnson to join the ticket as a progressive balance to Harding.[13] When Johnson turned down the offer, they approached Lenroot, who accepted.[13] However, when Illinois Senator Medill McCormick stood up to nominate Lenroot, several delegates began to shout for Coolidge.[13] Though initially he had only been nominated after the refusal of Senator Lodge (another Massachusetts man), a groundswell of support built up for Coolidge, who won the nomination over Lenroot; historian Donald R. McCoy called it the first time since the 1880 nomination of James Garfield that "the delegates had taken control of a Republican convention".[14] Coolidge, who was not at the convention during the vice presidential nomination, agreed to join the ticket.[13]
| Vice Presidential Balloting[15] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Candidate | 1st | Unanimous |
| Coolidge | 674.5 | 984 |
| Lenroot | 146.5 | |
| Allen | 68.5 | |
| Anderson | 28 | |
| Gronna | 24 | |
| Johnson | 22.5 | |
| Pritchard | 11 | |
| Not Voting | 9 | |
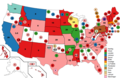
Vice Presidential Balloting / 5th Day of Convention (June 12, 1920)
-
1st
Vice Presidential Ballot
See also
[edit]- 1920 Democratic National Convention
- 1920 United States presidential election
- History of the United States Republican Party
- List of Republican National Conventions
- Margaret Hill McCarter
- 1920 Republican Party presidential primaries
- United States presidential nominating convention
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Margulies, Herbert F. (1977). "Irvine L. Lenroot and the Republican Vice-Presidential Nomination of 1920". The Wisconsin Magazine of History. 61 (1): 21–31. ISSN 0043-6534. JSTOR 4635197.
- ^ "Platform Adopted With Anti-Wilson League Plank; 'My Victory,' Says Johnson; Balloting Starts Today; Wood Men Claim the Lead; Midnight Move for Lowden". New York Times. 11 June 1920. Retrieved 9 October 2015.
- ^ Miller, Karen A.J. (1999). Populist Nationalism: Republican Insurgency and American Foreign Policy Making, 1918–1925. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 87–89. ISBN 9780313307768. Retrieved 9 October 2015.
- ^ https://chicagotribune.newspapers.com/image/355017021 Chicago Tribune, June 8, 1920
- ^ a b "Platform Fights Starts as the Convention Opens; Johnson Flatly Demands Repudiation of the League; Apathy in the Convention; Lodge Permanent Chairman". New York Times. 9 June 1920. Retrieved 9 October 2015.
- ^ a b c d "Text of the Republican Platform, Except League Plank; Dispute Over That, and Threat of a Bolt by Borah; Wood Men See Gains; New Yorkers Balk at Butler Pledge". New York Times. 10 June 1920. Retrieved 9 October 2015.
- ^ "Four Ballots, No Nomination, Wood Leads; Has 314 1/2 Votes, Lowden 289 and Johnson 140 1/2; Midnight Conferences Brings No Results". New York Times. 12 June 1920. Retrieved 9 October 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f "Harding Nominated for President on the Tenth Ballot at Chicago; Coolidge Chosen for Vice President". New York Times. 13 June 1920. Retrieved 9 October 2015.
- ^ a b Miller, pp. 90–91
- ^ A slightly different version appears in Andrew Sinclair, The available man: the life behind the masks of Warren Gamaliel Harding (1965) p. 136.
- ^ Richard C. Bain, and Judith H. Parris, Convention decisions and voting records (Brookings Institution, 1973).
- ^ Wesley M. Bagby, "The 'Smoke Filled Room' and the Nomination of Warren G. Harding." Mississippi Valley Historical Review 41.4 (1955): 657–74 online.
- ^ a b c d "Calvin Coolidge, 29th Vice President (1921–1923)". US Senate. Retrieved 9 October 2015.
- ^ McCoy, Donald R. (1967). Calvin Coolidge: The Quiet President. Macmillan. pp. 118–21.
- ^ Bain, Richard C.; Parris, Judith H. (1973). Convention Decisions and Voting Records. Brookings Institution. pp. 200–08.
Bibliography
[edit]External links
[edit]- Republican Party platform of 1920 at The American Presidency Project
- Harding acceptance speech at The American Presidency Project
| Preceded by 1916 Chicago, Illinois |
Republican National Conventions | Succeeded by 1924 Cleveland, Ohio |